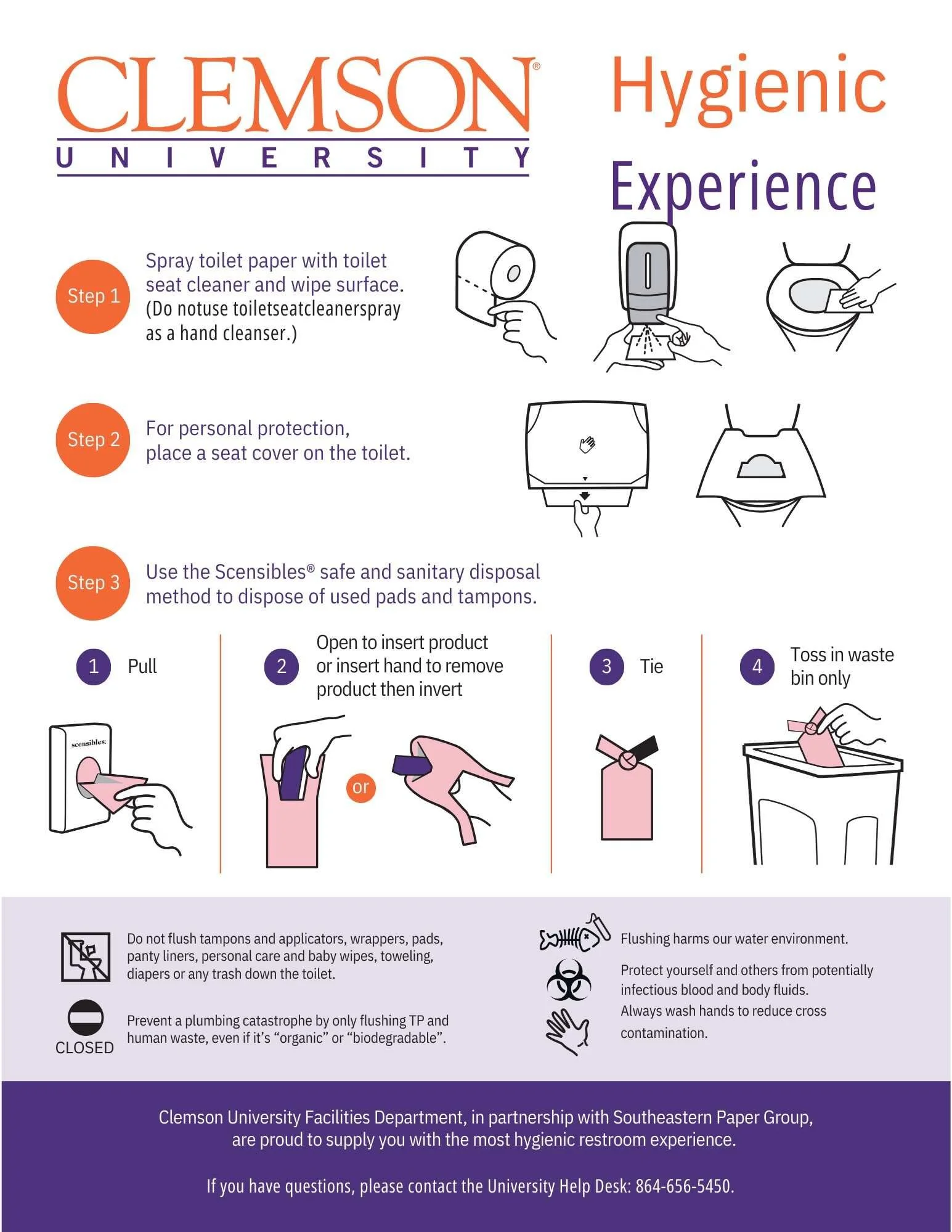
Case Studies in partnership with Hospeco Brands group
Scensibles® Personal Disposal Bags solve odor problem in airports women’s restrooms
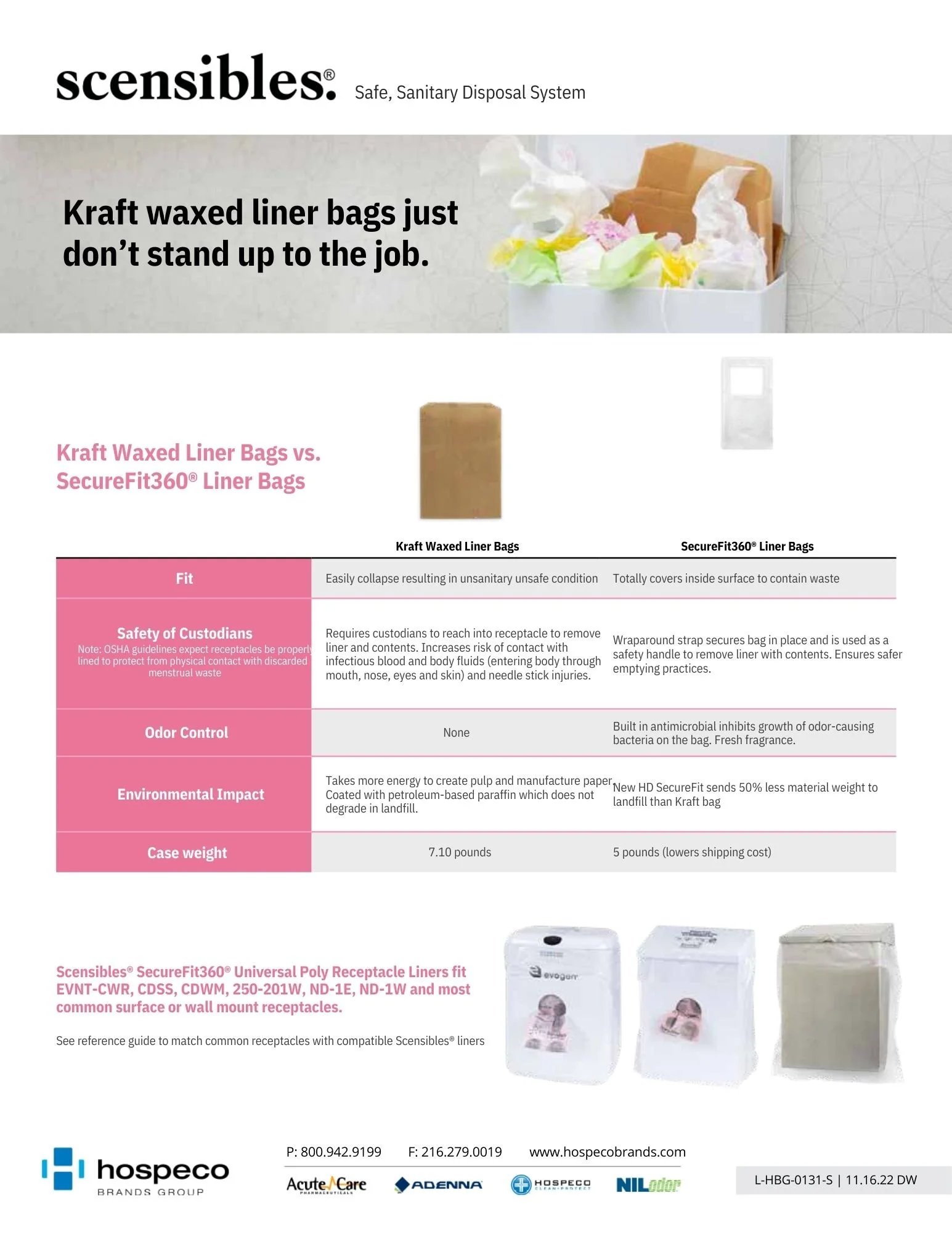
“OSHA expects the receptacles to be lined properly to prevent contact with soiled products. Best Cleaning Practices (approved by ISSA) recommend using only one liner bag to effectively cover the inside surface to totally contain waste.”
Best cleaning Practices: Feminine Waste Disposal Receptacles
written by ann germanow, Allen Rathey, Lynn Krafft, Perry Shimanoff
recognized and approved by International Sanitary Supply Association
Expectations of OSHA’s Blood borne Pathogens Standard
Facility Cleaning & Maintenance
Facility Cleaning & Maintenance
Cleanlink
Tackling Odor Issues In Women’s Restrooms
ISSA
Restrooms: Where Are the Germs Really?
Best Practices for Menstrual Care in Away-From-Home Restrooms
FacilitiesNet
Hospeco: Scensibles Bag Dispenser
OTHER
Suburban Outlaw celebrates Ann Germanow, co-founder of Scensibles
2014 Democrat and Chronicle